IoT (Internet of Things) isn’t just tech jargon or a passing fad. It’s a way to fix real problems, save time, and make money. But if this is a whole new world or you’re just trying to validate a concept, you might need some IoT Use Cases to help stir your imagination as to what’s possible.
If you’re running a business, especially in Ireland or the UK, and wondering what all the fuss is about, this guide is for you. I’ll break it down so it’s clear, practical, and worth your time.
Here’s what you’ll learn:
-The key ways businesses are using IoT today.
-How IoT can actually make or save you money.
-Where to focus if you’re thinking about diving in.
Let’s get into it.
What Makes IoT So Useful?

IoT connects devices to the internet to share data and automate tasks. Sounds fancy, but here’s the simple truth: IoT can cut through waste, stop small issues from snowballing, and keep you ahead of your competition.
Picture this: a farmer in Galway uses IoT sensors to track soil moisture. If it’s too dry, the system automatically waters the crops. No guessing, no overwatering, just results. That’s the power of IoT.
Real Life IoT Use Cases, Listed By Their Roadblock:
I’ve seen plenty of business roadblocks, but IoT can solve many of them—fast. Whether it’s saving time, cutting costs, or improving safety, IoT delivers measurable results. Here are a few standout examples:
Inefficient Warehouse Operations
Amazon faced challenges in its massive warehouses, struggling with inventory errors and delays. They tackled this by using IoT-enabled robots and sensors. These systems reduced picking errors by 40% and sped up order fulfillment by up to 50%, saving the company millions annually in operational costs.
Skyrocketing Energy Costs
British Gas implemented smart meters for real-time energy tracking, helping customers optimize their usage. On average, households saved 15-20% on energy costs annually. Across thousands of users, that’s millions in reduced waste and costs.
This can work for businesses too. Imagine reducing your electricity bill by 20%—could you fund an expansion with those savings?
Equipment Downtime
Imagine if your equipment could talk to you. Rolls-Royce utilized IoT-based predictive maintenance to monitor engine health, reducing unplanned engine maintenance events by up to 70% and achieving significant cost savings. With IoT, issues are identified early, keeping operations running smoothly.
Long Queues, Frustrated Customers
Disney introduced the MagicBand, an IoT-enabled wearable, to streamline guest experiences. This simple solution reduced wait times by up to 50% and increased guest spending by 8%. Wait times went down, sales went up, and customers walked away happier.
Fleet Management Chaos
UPS used IoT in their fleet management system to optimize delivery routes with real-time GPS and analytics. The results? 100 million fewer miles driven and 10 million gallons of fuel saved annually. That’s not just cutting costs—that’s transforming logistics.
Unsafe Worksites
Kinetic, a company specializing in wearable technology, introduced the Reflex device to monitor workers’ movements and provide real-time feedback to prevent injuries. This IoT solution led to a 50-60% reduction in injury frequency across industries like retail, logistics, and manufacturing.
IoT isn’t just fancy tech—it’s about solving real issues. If any of these sound like challenges your business is facing, drop me a message. Galvia Digital can help you make it happen.
Real Life IoT Use Cases, Listed By Their Solution:
Here are ten practical IoT applications transforming industries:
Real-Time Asset Tracking
Challenge: Misplaced inventory or equipment leads to operational delays and increased costs.
Solution: IoT sensors provide real-time location data for assets, enhancing inventory management and reducing losses.
Example: DHL implemented IoT-enabled tracking systems to monitor shipments globally, improving delivery accuracy and customer satisfaction.
KPIs Impacted:
- Reduced asset loss by 30%.
- Improved delivery times by 20%.
Source: DHL IoT Tracking
Predictive Maintenance

Challenge: Unexpected equipment failures cause costly downtime.
Solution: IoT sensors monitor equipment health, predicting maintenance needs before failures occur.
Example: Rolls-Royce uses IoT to monitor aircraft engines, predicting maintenance needs and reducing in-flight failures.
KPIs Impacted:
- Decreased unplanned downtime by 50%.
- Maintenance costs reduced by 30%.
Source: Rolls-Royce IoT Engines
Smart Energy Management
Challenge: High energy consumption increases operational costs.
Solution: IoT systems optimize energy use by adjusting lighting, heating, and cooling based on occupancy and usage patterns.
Example: The Edge building in Amsterdam uses IoT to manage energy, making it one of the most sustainable office buildings globally.
KPIs Impacted:
- Energy costs reduced by 70%.
- Achieved a 98.4% sustainability score.
Source: The Edge Amsterdam
Enhanced Customer Experience
Challenge: Meeting customer expectations for personalized and efficient service.
Solution: IoT devices collect customer data to tailor experiences and streamline services.
Example: Starbucks uses IoT to personalize offers and streamline mobile orders, enhancing customer satisfaction.
KPIs Impacted:
- Increased customer retention by 15%.
- Boosted sales through personalized offers by 10%.
Source: Starbucks IoT
Environmental Monitoring
Challenge: Maintaining optimal environmental conditions is crucial in industries like pharmaceuticals and food storage.
Solution: IoT sensors monitor factors like temperature and humidity, ensuring compliance and product quality.
Example: Pfizer uses IoT to monitor storage conditions of vaccines, ensuring efficacy and safety.
KPIs Impacted:
- Reduced product spoilage by 25%.
- Compliance incidents decreased by 40%.
Source: Pfizer IoT
Supply Chain Optimization
Challenge: Inefficiencies in the supply chain lead to delays and increased costs.
Solution: IoT provides visibility into the supply chain, enabling better planning and efficiency.
Example: Maersk uses IoT to monitor shipping containers, optimizing routes and reducing delays.
KPIs Impacted:
- Shipping delays reduced by 20%.
- Operational costs decreased by 15%.
Source: Maersk IoT
Smart Agriculture

Challenge: Traditional farming methods are resource-intensive and less efficient.
Solution: IoT enables precision farming through data-driven decisions on irrigation, fertilization, and pest control.
Example: John Deere’s IoT-enabled equipment provides farmers with data to optimize crop yields.
KPIs Impacted:
- Crop yields increased by 10%.
- Water usage reduced by 15%.
Source: John Deere IoT
Fleet Management

Challenge: Managing a fleet of vehicles efficiently is complex and costly.
Solution: IoT devices track vehicle locations, monitor driver behavior, and optimize routes.
Example: UPS leverages IoT for route optimization and package tracking. Their system uses real-time data to reduce travel distances, fuel consumption, and delivery times.
KPIs Impacted:
- Fuel consumption reduced by 10%.
- Delivery times improved by 15%.
Source: UPS IoT Optimization
Smart Cities: Intelligent Waste Management
For smart cities, IoT powers everything from traffic management to public safety, air quality monitoring, and smart waste collection.
For now, we’ll focus on one specific use: Intelligent Waste Management.
Challenge: Inefficient waste collection leads to increased costs and environmental issues.
Solution: IoT-enabled smart bins monitor fill levels and send alerts for optimized waste collection schedules.
Example: The city of Dublin implemented IoT in waste management, reducing the frequency of unnecessary pickups and improving cleanliness in public spaces.
KPIs Impacted:
- Waste collection costs reduced by 30%.
- Improved public satisfaction with cleaner environments.
Source: Dublin Smart Waste
Environmental Monitoring: Industrial Emissions
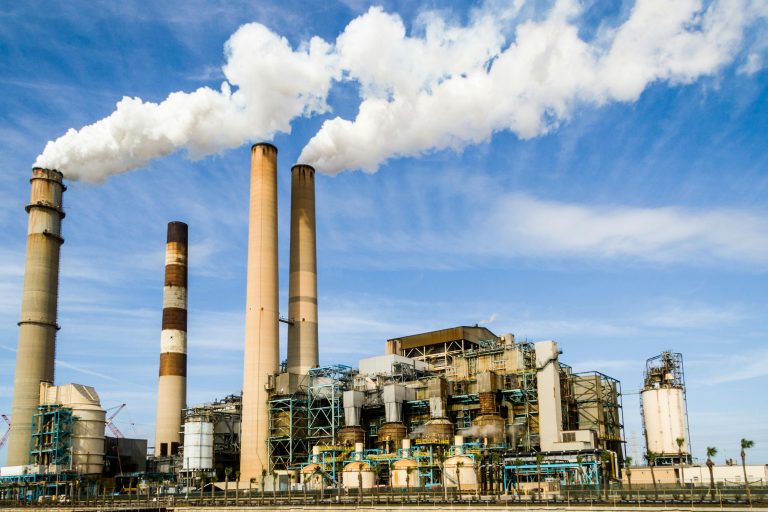

Challenge: Ensuring compliance with strict environmental regulations and avoiding penalties.
Solution: IoT sensors continuously monitor industrial emissions and alert operators when limits are breached, enabling corrective action.
Example: Shell uses IoT to monitor emissions at refineries, ensuring compliance and reducing carbon footprint.
KPIs Impacted:
- Regulatory fines reduced by 25%.
- Improved sustainability metrics reported to stakeholders.
Source: Shell Emissions Monitoring
Industry-Specific IoT Use Cases
IoT shines brightest when it’s tailored to your industry. Here’s a more comprehensive look at how IoT is creating value across different sectors:
Manufacturing (Optimize):
Monitor machine performance to reduce downtime and boost efficiency.
Implement predictive maintenance systems to prevent costly failures.
Automate supply chain tracking to reduce lead times and improve accuracy.
Enable robotics integration for smarter assembly lines.
Healthcare (Monitor):
Track patient vitals in real time with IoT-enabled wearable devices.
Automate medication reminders and remote diagnostics for better care.
Enhance hospital asset management by tracking medical equipment usage.
Use IoT to predict and manage hospital occupancy rates efficiently.
Oil & Gas (Secure):
Detect pipeline leaks early with IoT sensors, minimizing environmental damage.
Monitor equipment in remote locations to ensure safety and operational efficiency.
Optimize energy usage across drilling sites with IoT analytics.
Enhance worker safety with connected devices that monitor hazardous conditions.
Retail (Enhance):
Use IoT to track customer preferences and personalize shopping experiences.
Streamline inventory management with real-time stock updates.
Enable cashier-less checkout systems for faster customer experiences.
Enhance security with smart monitoring of stores and warehouses.
Logistics (Streamline):
Optimize delivery routes using IoT tracking for faster, more efficient shipments.
Monitor the condition of perishable goods during transit to reduce losses.
Enable real-time communication between drivers and dispatchers for smoother operations.
Automate fleet maintenance scheduling based on IoT data.
Agriculture (Grow):
Automate irrigation systems using IoT sensors to conserve water and boost yields.
Monitor soil health and weather conditions to make data-driven farming decisions.
Track livestock health and location using connected devices.
Predict and mitigate pest infestations with IoT-enabled monitoring systems.
More comprehensive industry-specific use cases can be found on each of their respective pages—just click above!
How to Get Started with IoT
Getting started with IoT doesn’t have to be daunting. Here’s how to break it down:
1. Pinpoint a Problem
Identify a specific challenge your business is facing. For example, do you struggle with equipment downtime? Inventory management? Customer retention? Focus on one area where IoT can make a measurable impact.
2. Start Small
You don’t need a massive overhaul. Begin with a small, testable project. For instance, set up IoT sensors to monitor one machine, a single shipment, or one store location. Measure the results before expanding further.
3. Partner with Experts
IoT involves a mix of hardware, software, and data analytics. Collaborate with specialists, like Galvia Digital, who have experience tailoring IoT solutions to businesses like yours.
4. Define Your KPIs
What does success look like? Whether it’s reduced downtime, better energy efficiency, or faster delivery times, set clear metrics to track progress and ROI.
5. Plan for Scalability
Once your pilot project succeeds, expand your IoT implementation to other areas. Use the lessons learned to refine your approach and scale effectively.
Ready to See How IoT Can Work for You?
At Galvia Digital, we specialize in designing and delivering IoT solutions tailored to your business needs. Whether you’re looking to optimize your operations, reduce costs, or enhance customer experiences, we’ve done it before—and we can do it for you.
Let’s make it simple. Reach out today for a no-obligation chat, and we’ll show you practical ways IoT can drive real results for your business.
Book a Call With Us Today!
IoT Use Cases FAQ
What is IoT and its use cases?
IoT, or the Internet of Things, connects devices to the internet, allowing them to share data and automate tasks. Use cases range from real-time asset tracking in logistics to precision farming in agriculture and even smart home systems that save energy.
In which cases is IoT used?
IoT is used across a wide range of scenarios:
- Smart Cities: Traffic control, air quality monitoring, waste collection.
- Smart Homes: Security cameras, smart lights, energy management.
- Healthcare: Patient monitoring, wearable devices, and hospital management.
- Retail: Inventory tracking, personalized shopping experiences, and cashier-less checkout.
- Agriculture: Automated irrigation, soil condition monitoring, and livestock tracking.
- Supply Chain Management: Tracking shipments and optimizing delivery routes.
- Energy & Utilities: Smart grid management, energy optimization, and predictive maintenance.
Where is IoT used in daily life?
IoT is everywhere in modern life. Some examples include:
- Smart home devices: Thermostats like Nest, smart plugs, or voice assistants like Alexa.
- Wearable tech: Fitness trackers like Fitbit and Apple Watch.
- Connected vehicles: Cars with real-time GPS and performance monitoring.
- Healthcare: Devices like glucose monitors or sleep trackers.
Which is the critical IoT use case?
Predictive maintenance stands out as one of the most critical IoT use cases. It helps industries like manufacturing, aviation, and energy reduce downtime by addressing equipment issues before they occur. This can save millions annually in operational costs.
What are 5 examples of IoT devices?
- Smart thermostats (e.g., Nest).
- Fitness trackers (e.g., Fitbit).
- Smart security cameras (e.g., Ring).
- Connected cars (e.g., Tesla).
- Smart refrigerators (e.g., Samsung Family Hub).
How does Coca-Cola use IoT?
Coca-Cola integrates IoT into its vending machines. These machines monitor stock levels, identify maintenance needs, and even tailor drink recommendations to customer preferences.
Source: Coca-Cola IoT Vending Machines
How does Tesla use IoT?
Tesla leverages IoT to enhance vehicle performance and customer experience. IoT powers Tesla’s autopilot, over-the-air software updates, and real-time data monitoring for predictive maintenance.
Source: Tesla IoT Connectivity
How is IoT used today?
IoT drives innovation across industries:
- Smart Cities: Managing urban traffic and waste collection.
- Healthcare: Wearable monitors and remote diagnostics.
- Retail: Personalized offers and stock management.
- Agriculture: Soil monitoring and automated watering systems.
- Energy: Optimizing power usage and enabling smart grids.
Which industries use IoT the most?
IoT adoption spans various industries, but some of the most active include:
- Smart Cities: Traffic control, air quality, waste management.
- Smart Homes: Energy management and security.
- Supply Chain Management: Asset tracking and shipment monitoring.
- Agriculture: Precision farming and livestock monitoring.
- Enterprise Solutions: Office automation and employee productivity tools.
- Wearables: Fitness trackers and health monitors.
- Connected Factories (Industrial IoT): Robotics, predictive maintenance.
- Retail: Inventory control and cashier-less checkouts.
- Hospitality: Smart room controls and energy management.
- Traffic: Smart signals and congestion tracking.
- Fleet Management: Route optimization and real-time tracking.
- Energy & Utilities: Smart grids and energy conservation.
- Healthcare: Remote patient monitoring and predictive diagnostics.



Social Profiles